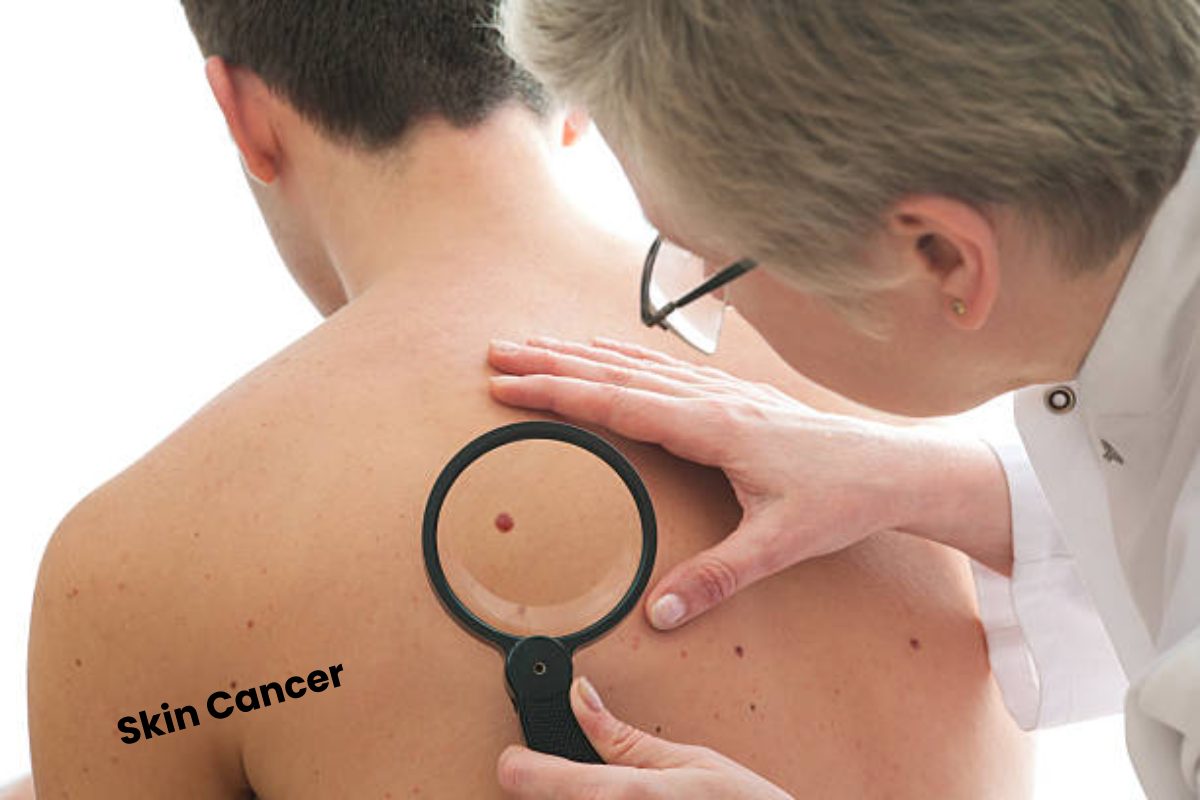
Skin cancer is, without a doubt, the most common type of cancer. When it’s small and hasn’t spread, finding it initially makes skin cancer easier to treat.
Some doctors and other health specialists include skin exams as routine checkups. Many doctors also recommend examining your skin about once a month.
Examine your skin in a bright room in front of a full-length mirror. Use a hand mirror to explore areas that are hard to see. Squamous and Basal cell skin cancers are more mutual than melanomas.
Both basal and squamous cell carcinomas or cancers usually grow in areas more exposed to the sun. However, they can appear anywhere.
Table of Contents
Basal Cell Carcinomas – What To Watch For
- Flat, firm, whitish or yellow areas, similar to a scar.
- Red, raised areas that may be itchy.
- Small translucent, shiny, pearly bumps in shades of pink and red that may have bluish, brownish, or darker areas.
- Open sores (which may have weeping or crusty areas) do not heal or reopen after they have healed.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas – What To Watch For
- Rough or reddish and scaly areas may crust or bleed.
- There are raised growths or lumps, often with an indented (lower) area in the centre.
- Open sores (which may have weeping or crusty areas) do not heal or reopen after they have healed.
- Wart-like growths.
However, not all skin cancers look like these descriptions. So show your doctor anything that concerns you, including:
- Any new stain
- Any spot that doesn’t look like the other spots on your body
- Redness or new swelling above the edge of a mole
- Discolouration that spreads from the edge of a spot to the surrounding skin
- Itching, pain or tenderness in a skin region that does not stop or constantly resurfaces.
- Any sore (ulcer) that does not heal
- Mole surface changing – oozing, peeling, bleeding, or the appearance of a bulge or bump.
What Causes Skin Cancer?
The two leading causes of skin cancer are the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays and the use of tanning booths. However, recent research studies have shown that tanning booths during adolescence increase up to 2 times if you have done more than ten sessions in your life.
In addition to the factors previously described, there are also other risk factors such as:
- We have more than 50 moles on the entire body or more than 3 moles with atypical features.
- Genetic factors (that is, mutations in specific genes or family history)
- History of radiotherapy
- Certain conditions that suppress the immune system
- Exposure to high levels of arsenic.
Melanoma – Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a malignant tumour that develops from melanocytes, specialized skin cells whose primary function is melanin production (tan). Melanin is our defence mechanism against the sun’s ultraviolet rays. Due to its great malignant potential, it is responsible for more than 90% of deaths from skin cancer.
This tumour mainly affects the skin, but it can also develop in the mucous membranes (vaginal, oral, conjunctival) and inside the eye. Usually, melanomas develop on healthy skin approximately 20-30% of the time, and they can grow on a pre-existing mole (nevus).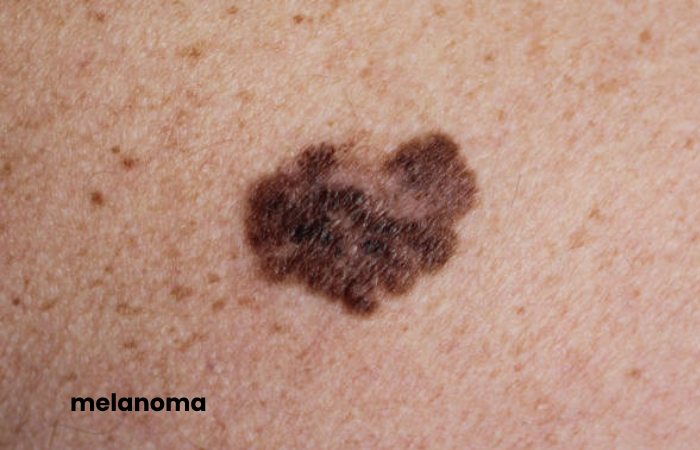
Basal Cell Carcinoma
It is the most common cancer in humans. This carcinoma usually grows on parts of the skin that have received a lot of sun. This type of cancer begins as small, shiny bumps or pimples, usually on the nose or other face parts. But you can have it anywhere on your body, including your trunk, legs, and arms. If you have light skin and eyes, you will most likely get this skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma usually grows gradually and often does not appear for many years after intense or prolonged sun exposure. You can get it at a younger age if you spend a lot of time in the sun or use tanning beds.
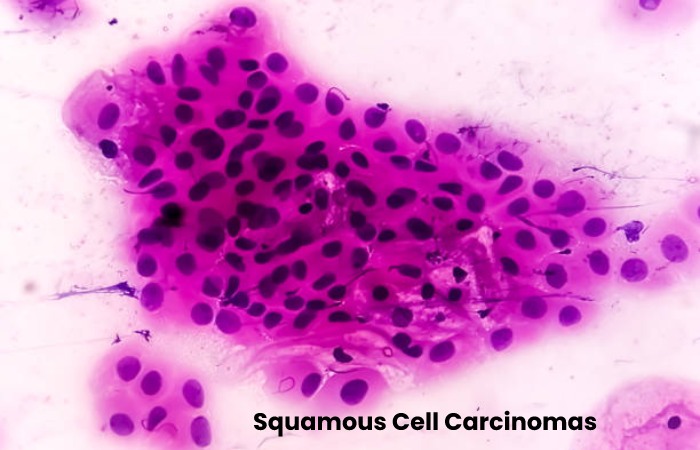
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
It is another type of skin cancer. It is common in areas of the body damaged by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds.
Squamous cell carcinoma usually grows reasonably slowly and locally. In rare cases, when it has been evolving for a long time, or we have risk factors (immunosuppression, transplant patients), it can spread to nearby tissues, bones and lymph nodes, where it can be challenging to treat. However, most cases are caught early and are easy to treat.
How Is Skin Cancer Treated?
The good news is that if malignant skin tumours are detected early, the dermatologist can treat them with little or no scarring and with a good chance of eradicating them.
Often, the specialist can even detect the neoplasm at a precancerous stage (in situ) and apply minimally invasive treatments or even creams to cure it. That is why you must know the different types of skin cancer to offer you a curative treatment.
On the other hand, melanoma will require a specific treatment based on the size of the tumour and the involvement it may have had in other organs.
Conclusion
What are the Types of Skin Cancer? How to detect them – Cancers are one of the deadliest diseases. Many people around the world are suffering from this fatal disease. Different types of cancer are related to other parts of the body. Skin cancers are affected by the skin surface. To sum up, there are different types of skin cancers.
Related Searches –
[skin cancer pictures]
[skin cancer symptoms]
[skin cancer pictures early stages]
[skin cancer treatment]
[skin cancer types]
[is skin cancer deadly]
[skin cancer images nhs]
[early-stage skin cancer]