Lump Behind Ear – The Ear can develop for a variety of causes. While most chunks are harmless, they can infrequently indicate a more severe ailment. The Ear can be both firm and soft. Some may be painful to the touch, while others are not. Let’s look at some reasons for ear lumps, possible treatments and when to contact a doctor.
Table of Contents
Common Infections be able to Cause Lumps Behind Ear
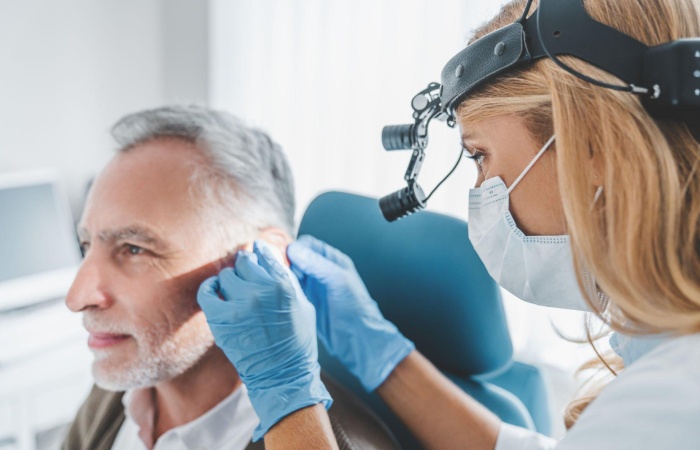
Doctor examining area behind man’s Ear –
Ear lumps are commonly produced by colds, the flu, strep throat, or respiratory infections. Because infection can enlarge and irritate the lymph nodes behind your ears. Swollen glands are typically not causing concern.
They will probably resolve on their own or, if produced by a bacterial infection, can be readily treated with medication. For any discomfort, your doctor may also suggest over-the-counter pain medicine. These are easily accessible at Smith’s Drug Store or any nearby drugstore.
The lymph nodes may become very big, swollen, red, and sensitive if the infection is severe.
Mastoiditis is a dangerous infection that can create a bulge behind the Ear. Mastoiditis is bacterial pollution of the mastoid bone situated behind the Ear. It frequently happens when an infection in the middle Ear goes untreated and spreads. Mastoiditis can occur at any age, although it is more common in children. Mastoiditis symptoms include:
Pain behind the Ear that is excruciating
Drainage of the ears
Fever \Headache
Lump Behind Ear: Causes, Treatments, and Risks
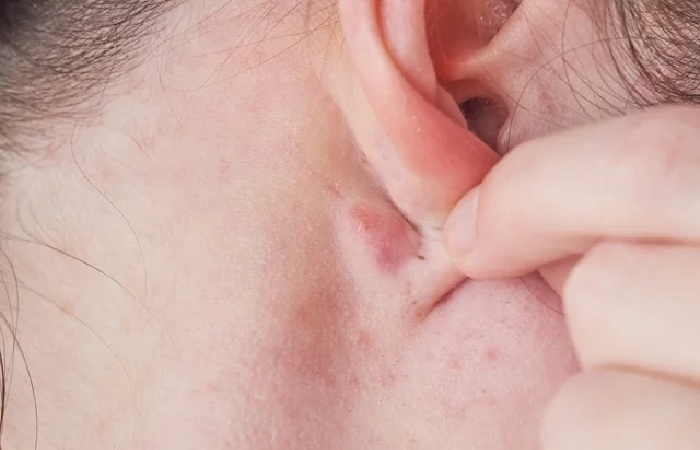
Discovering a lump behind your Ear can be alarming, partly because it’s so difficult to get a first-class look at what’s happening.
While it’s always an excellent plan to have a healthcare provider examine any new bump on your body, know that, most of the time, a lump behind the Ear isn’t caused for concern.
In this article, I’ll look at the most common and most serious possible causes of lumps that appear behind the Ear. Then I’ll discuss how you can perform a self-check of any growths that appear in this area and how your doctor will check any lumps to arrive at a diagnosis. Lastly, I’ll overview treatment options for Lump Behind Ear the Ear and explain when to see a doctor about this issue.
Lump Behind Ear Possible Causes
There are many likely causes for a lump behind the Ear. To distinguish between these potential explanations, doctors will first try to identify the kind of lump.
Possibilities include a cyst, pimple, tumour, swollen lymph node, or carcinoma. Some of these growths are associated with more deadly cancers or rare genetic disorders.
But most Lump Behind Ear the ears are common cysts typically associated with less-threatening skin issues.
Most common causes:
Many Lump Behind Ear the ears arise when something prevents dead skin cells from shedding, or oil glands become blocked.
Then skin cells or oil can build up below the skin’s upper surfaces, creating masses called cysts.
Though mostly benign, these skin cysts can become unsightly or uncomfortable, especially if they grow more significant than a pimple. They can also cause pain, become infected and filled with pus, or rupture. Two of the most common cysts growing behind the Ear are sebaceous cysts and epidermoid cysts.
Sebaceous cysts: These sack-like lumps form when dead skin cells chunk the sebaceous oil glands attached to skin follicles. These blockages cause a buildup of sebum (a.k.a. oil). Sebaceous cysts share similarities with acne pimples and whiteheads. However, they are larger, grow slowly, and rupture differently.
Epidermoid cysts: These lumps arise from a blockage when the skin’s surface folds around a hair follicle opening (a.k.a. pore). This causes dead hide cells to build up, forming a lump.
A swollen lymph node is the third common reason for swelling behind the Ear. That is usually related to a localized infection or irritation and resolves once the offending agent is removed or treated. In some cases, this could signal something more serious, so see a healthcare provider be sure.
More serious causes
Lump Behind Ear – The Ear can also have more severe or uncommon causes, including the following:
Basal cell carcinoma: This slow-growing skin cancer can look and feel like a small, pearly bump that sometimes resembles a mole or a pimple.
Squamous cell carcinoma: This sometimes looks like an open sore with a raised border; other times, it seems like a wart.
Temporal bone tumours: In some rare cases, basal or squamous cell skin cancer can spread to the part of the skull bone that’s behind the ears and cause these bumps.
Gorlin syndrome: People with this rare genetic disorder develop tumours, cysts, and skin pits all over their bodies, sometimes behind the ears.
Gardner syndrome: It is another rare genetic disorder that can lead to thousands of polyps and cysts throughout the body. While most form in the colon, cysts can form in other locations, including behind the Ear.
Infections: Viral, fungal, and bacterial infections may cause unusual swollen patches behind the Ear.
GET STARTED
Self-Check and Diagnosis Guide
The best way to self-check an ear lump is to sit or stand in an area with good lighting and use mirrors to check the bump as well as possible.
Note if the lump is:
- Growing
- Hard and immovable
- Painful or tender to the touch
- Red, itchy or inflamed
- Leaking foul-smelling fluid
If any of this applies, see a healthcare provider.
In addition to a physical exam, they may order a biopsy to test for the presence of cancer or skin culture to see if the lump can be traced to a particular kind of infection.
A biopsy means they will remove a small amount of skin to examine under a microscope; a skin culture calls for swabbing an open cyst to collect a sample to test.
Possible Treatment
- Most Lump Behind Ear the Ear are slow-growing and noncancerous.
- Sometimes they shrink or vanish on their own.
However, treatment is necessary if an ear lump is infected or cancerous.
Treatment for infected lumps: Steroid injections, oral antibiotics, or draining the painful swelling may help eliminate the infection.
Treatment for cancerous lumps: Surgery is the preferred treatment method for any harmful cyst, carcinoma, or other growth. Surgery can also remove pesky noncancerous bumps. Radiation therapy may be used as a secondary treatment.
When to See a Medical Provider
Make a scheduled time to see a healthcare provider if you notice any new developments behind your ears.
Although most are cystic nodules and most cystic nodules are not harmful, some skin cancers look like cystic nodules or may develop alongside them and should always be checked.
Also, seek medical attention if the lump behind your Ear becomes painful, red, itchy, or inflamed, as these may be signs of infection.
Lump Behind the Ear: Possible Causes Explained
Not Always Cause for Concern
A lump behind the Ear is typically innocuous and simple to cure, and it is not necessarily indicative of a significant or long-term condition. This is common with enlarged lymph nodes, infections, and skin diseases that cause Lump Behind Ear the Ear.
Tumours can grow behind the Ear less often. These tumours can be benign; such as a mastoid osteoma, or malignant, such as parotid (salivary) gland malignancies. 2 In certain situations, they may begin as little, soft areas that expand to become more significant and more challenging.
This article goes through the most frequent symptoms and causes of a bulge behind the Ear. It will assist you in determining when you should see a healthcare practitioner and what some of the treatment options are.
Summary
There are various probable reasons for a bulge behind the Ear. Most of the time, the reason is something minor that will require resolution on its own or with minimum therapy. If the lump aches, grows or is accompanied by other indications, it should be examined by a medical practitioner.
Tumours behind the Ear can occur in rare circumstances and require extensive treatment. It is critical to notify your healthcare professional if you consume a lump behind your Ear or other symptoms, especially if they appear abruptly.
Related Searches:
pea-sized lump behind ear lobe painful
pea sized lump behind ear lobe no pain
hard lump behind ear on skull no pain
sore lump behind ear
small lump behind ear
hard painless lump behind ear
lymph nodes lump behind ear
lump behind ear child
hard painless lump behind ear
hard lump behind ear on skull no pain
lump behind ear on bone

